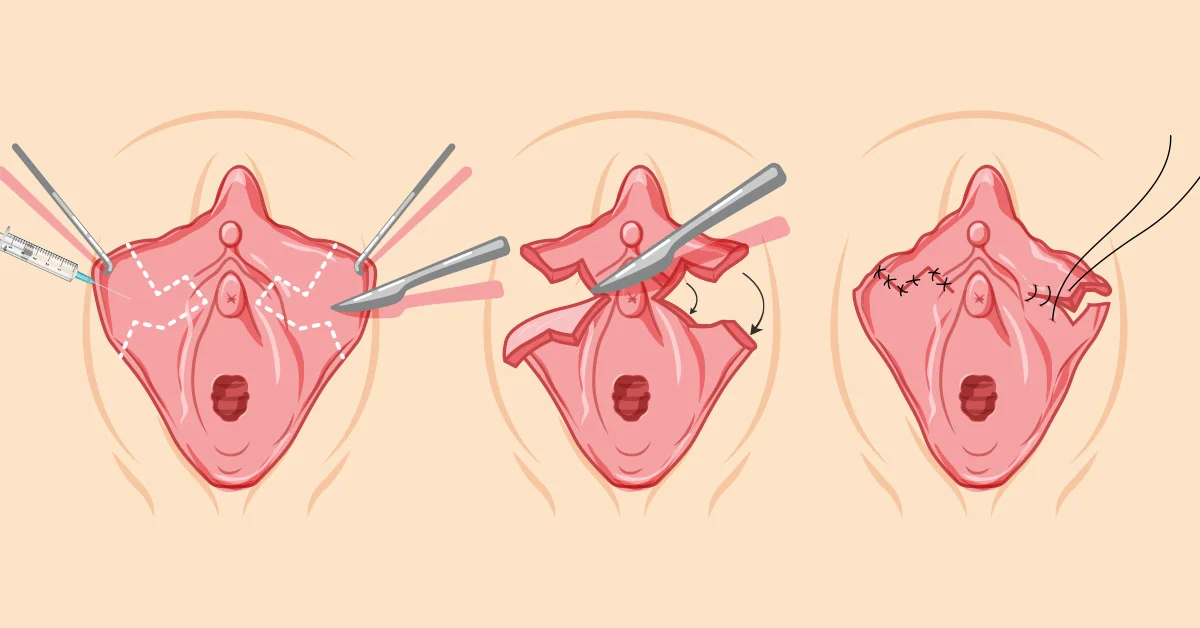
Over the years, several distinct techniques have evolved for performing the labiaplasty procedure. The decision of which method to apply must be considered carefully. This is because, once the procedure has been performed, it may be challenging or even impossible to carry out a revision procedure and might leave the patient with a permanent deformity. The choice of which method to be used should be left to a highly skilled cosmetic surgeon with great expertise in carrying out various surgical techniques based on each patient’s peculiarities and preferences.
What is the Z-Plasty Labiaplasty Technique?
The Z-plasty technique is a modification of the wedge labiaplasty. It is performed when there is excessive labial tissue where the labia minora inserts at the prepuce and/or the perineum and in cases of asymmetry or scarring.
It is a surgical technique in which a series of triangular incisions are made on the labia minora, followed by repositioning the labial tissues in a zig-zag pattern.
Key Considerations for the Z-plasty Labiaplasty Technique
- The Z-plasty technique was developed to help solve the issue of scar shortening/contracture encountered with the use of the wedge technique
- It can be performed where the patient has asymmetrical labia minora and/or excess redundant labia minora
- It should only be performed if the surgeon has the necessary skills and is comfortable performing the procedure.
It is essential to know that this technique is only ideal for some labiaplasty procedures.
The Z-plasty Labiaplasty Procedure
Preoperative Assessment
This includes:
- Discussion between the surgeon and the patient on the anticipated results and the technique to be used, including the pros and cons of the technique chosen.
- Before and after photographs of the procedure, especially for medico-legal reasons.
- Performing the procedure when the woman is not menstruating.
- Shaving of the perineum prior to surgery.
- Administration of antibiotics prior to the procedure.
- Obtaining verbal and written informed consent prior to the surgery.
Intraoperative Procedure
The procedure can be performed as an in-office procedure under conscious sedation and/or with local anesthetics or at the operation theatre under general or regional anesthesia.
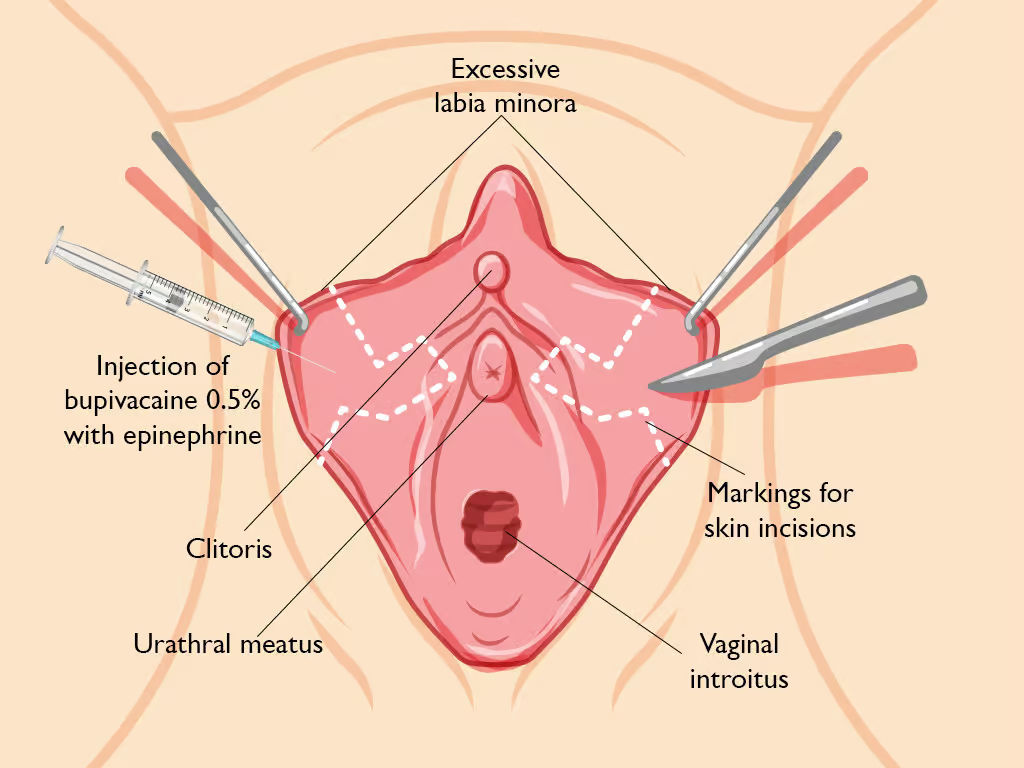
The patient is placed in a dorsal lithotomy position, and routine cleaning and draping is done. Each labia minora is gently grasped with clamps, and using a sterile marker, 90-degree Z plasties are drawn on the medial surface of the upper third of the labia minora. The surgeon ensures the two “Zs” converge towards the urethral meatus. This area is then infiltrated with a local anesthetic mixed with adrenaline to prevent bleeding.
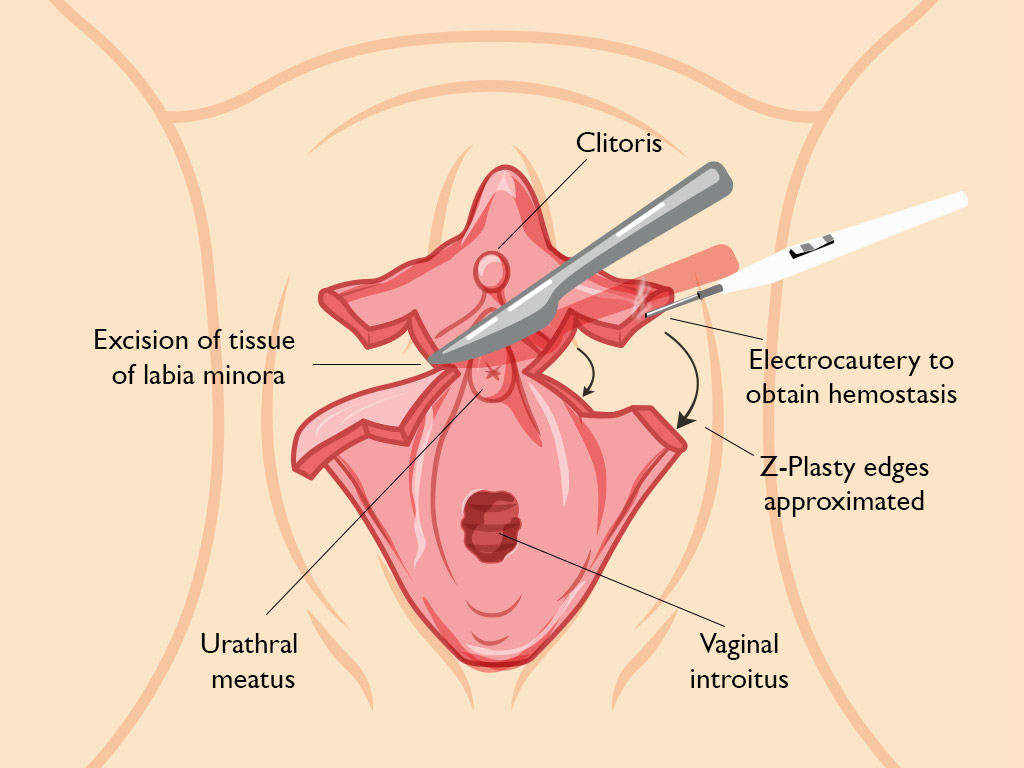
A scalpel, Laser or Radiofrequency device is used to excise this marked portion of the labia minora, and electrocautery may be used to ensure hemostasis. The inferior and superior portions of the labia are then rotated toward each other, and the edges are apposed using either interrupted or continuous absorbable 3/0-5/0 sutures e.g. vicryl sutures.
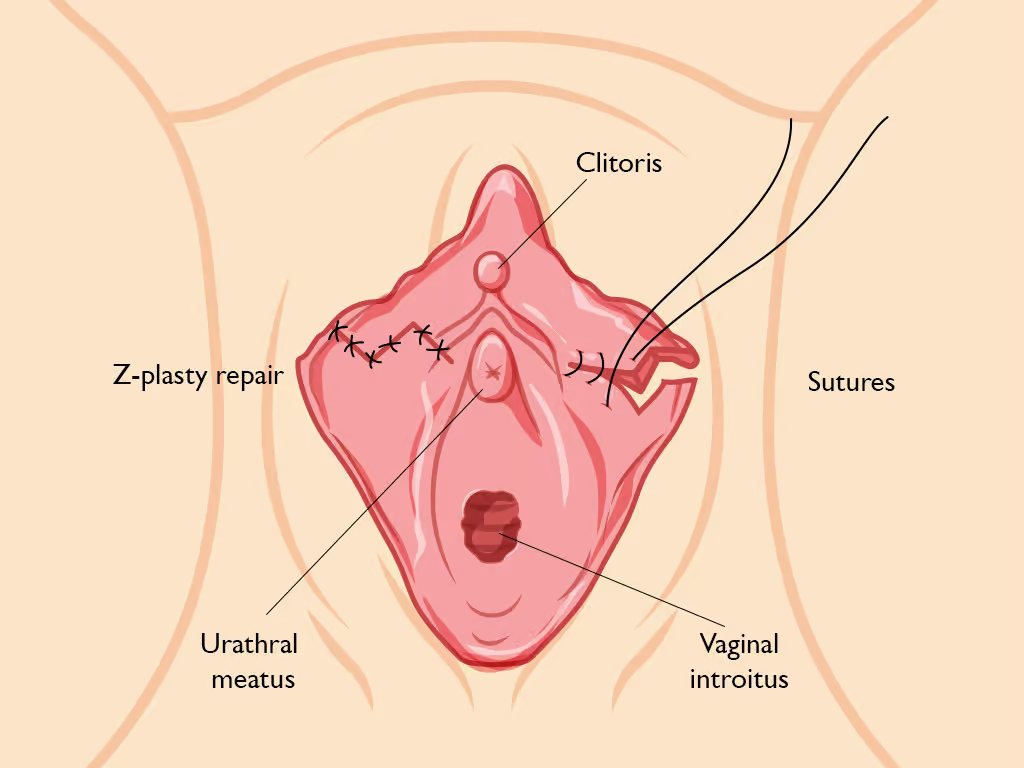
Wound dressing is applied over the operation site to protect it and promote healing.
Postoperative Care
The postoperative care for this technique is similar to that for other techniques;
- Analgesics and antibiotics should be administered to help manage pain and prevent infections following the procedure.
- Use of cold compress or an ice pack for about 15-20 mins several times a day to help reduce swelling and relief pain
- Use of a squirt bottle to help keep the area clean and dry so as to prevent infection.
- Avoiding tight-fitting clothing that could rub against the surgical site.
- Avoiding strenuous activities and prolonged standing as this encourages edema at the surgical site
- Avoiding penetrative activity such as tampon insertion or sexual intercourse for about six weeks after the procedure.
Advantages of the Z-plasty Labiaplasty Technique
- This technique maintains the natural contour and colour of the labia minora.
- Unlike wedge labiaplasty, it aims to reduce the tension on the suture site, thereby promoting healing and reducing the risk of dehiscence/breakdown.
- It can be tailored to meet the specific need and goals of each patient; this is because the surgeon can vary the size and shape of the incisions based on the individual’s anatomy and cosmetic preferences.
Disadvantages of the Z-plasty Labiaplasty Technique
- It is a more complex and time-consuming procedure than other techniques because it involves placing multiple incisions and carefully repositioning the tissue.
- This technique is associated with a higher risk of complications e,g, bleeding and infection. This is because the zig-zag incisions expose more tissues and cut more vessels.
- Use of this technique is associated with a longer recovery time. Patients who have labiaplasty using this technique tend to experience discomfort, swelling and bruising for a longer period of time.
- While this technique claims to minimize scarring, there is still a risk of visible scarring after the procedure.
Risks/Complications Associated with the Z-Plasty Labiaplasty Technique
Complications associated with the use of this technique are similar to other techniques and include;
- Pain and discomfort
- Bleeding
- Hematoma formation
- Infection
- Scarring
- Loss of sensitivity/Numbness
- Asymmetry
- Unsatisfactory results
- Poor wound healing/dehiscence
Irrespective of the technique, in order to minimize the risks and complications, it is crucial to get a labiaplasty performed by an expert surgeon with high experience.
Recovery Timeline Following the Z-plasty Labiaplasty Technique
Like any other labiaplasty recovery, this varies depending on the individual and the extent of the procedure.
- Immediately after the surgery, the patient may experience pain, swelling and bruising at the surgical site. Analgesics and bed rest may help manage these symptoms.
- In the first week after surgery, the patient will need to avoid any activity that puts undue pressure on the surgical site, e.g. exercise, sexual intercourse, or bicycle riding. Also, good hygiene and the use of ice packs will help in reducing the swelling that is present during this period.
- By the second week, the client can gradually resume most of her routine activities; however, it is advisable to stay clear of any activity that will put pressure on the surgery site.
- By the third week, most of the oedema must have subsided, and a clearer image of how the labia minora will look can be seen. It is advised that any penetrative activity should still be avoided.
- By the sixth week and beyond, most patients can resume their normal activities, including exercise and penetrative activities. However, before this is done, the patient must consult with the surgeon and obtain clearance.
For more information on labiaplasty techniques and procedures, contact us or schedule a no-obligation examination with our leading OB-GYN expert.