Table of Contents:
- Overview
- Definition and Types of Labial Asymmetry
- How Common Is Labial Asymmetry
- Causes of Labial Asymmetry
- Signs of Concern
- When To Seek Medical Advice
- Physical, Psychological and Social Aspects of Labial Asymmetry
- Treatments and Solutions for Labial Asymmetry
- Risks/Complications Associated With a Labiaplasty
- Professional Treatment For Labial Asymmetry
- References
The human body is unique, and the genitalia are no different. Like other paired body parts such as breasts, feet, and hands, the labia can vary in size and shape. Many women may notice that one side of their labia is larger than the other and wonder if this is normal or indicative of an underlying issue. This asymmetry can also lead to physical and psychological discomfort, impacting self-esteem and confidence.
Individuals are increasingly seeking medical and surgical intervention due to concerns regarding the appearance of their external genitalia. However, understanding the reasons behind this natural variation can provide reassurance and clarity. This article discusses labial asymmetry, exploring its causes, implications, and available treatments.
Definition and Types of Labial Asymmetry
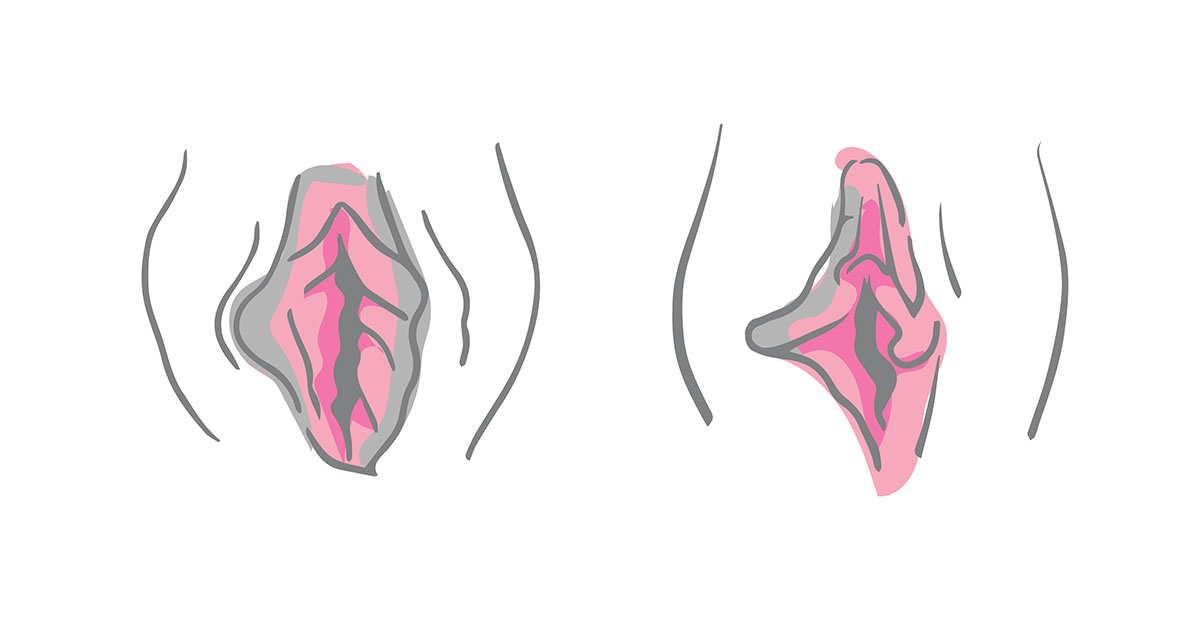
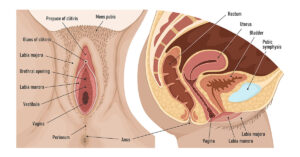
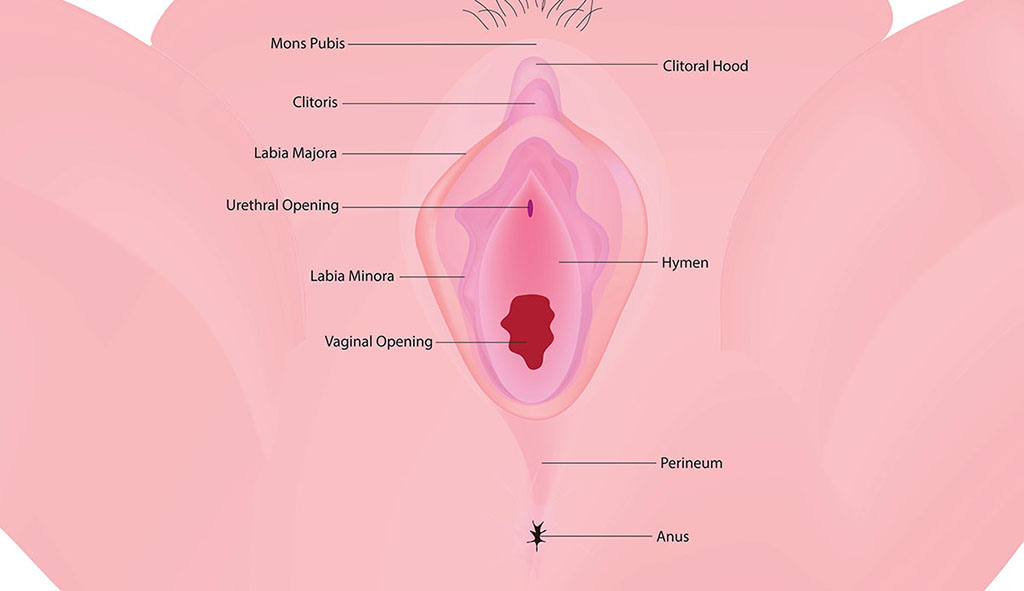
Labial asymmetry refers to a condition where one labium (lip) of the vulva differs in size, shape, or appearance from the other. This can occur in the labia majora (the outer lips) or the labia minora (the inner lips).1
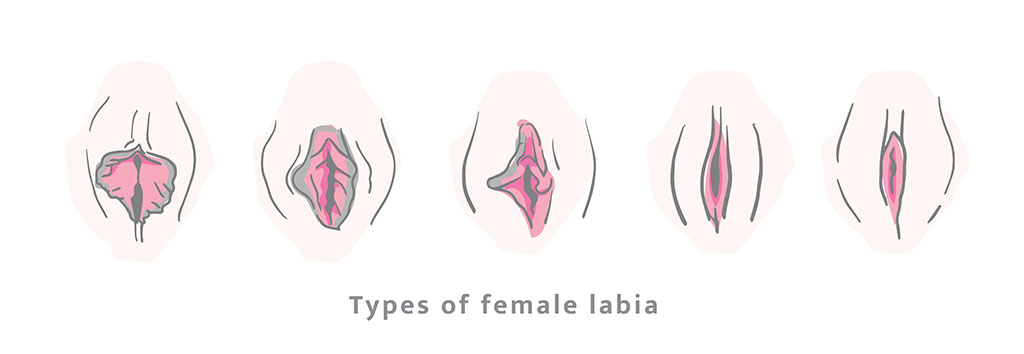
While the labia are meant to provide protection to the vaginal and urethral openings, their appearance can vary significantly from one woman to another, and slight asymmetry is common and usually normal. Below are the various types of labial asymmetry1:
Types of Labial Asymmetry
Size Asymmetry
- Labia Majora: One outer lip is larger or thicker than the other.
- Labia Minora: One inner lip extends further or appears larger than the other.
Shape Asymmetry
- Labia Majora: Differences in the contour or fullness of the outer lips.
- Labia Minora: Variation in the edges or contours of the inner lips, such as one side being more wrinkled or smooth.
Colour Asymmetry
Differences in pigmentation between the two sides, which can be influenced by hormonal changes, friction, or genetic factors.
Positional Asymmetry
One labium may sit higher or lower relative to the other, creating a noticeable difference in their alignment.
Surface Irregularities
One side may be rougher or more pronounced in terms of skin folds than the other.
How Common Is Labial Asymmetry?
A study by Lloyd et al. (2005) involving clinical assessments of female genital appearance revealed that the majority of women have some degree of labial asymmetry. The research emphasized that this variability is normal and typically not a cause for medical concern unless accompanied by discomfort or other symptoms.1
A comprehensive review by Gulia et al. (2017) on labia minora hypertrophy, which often includes asymmetry, highlighted that this condition can be found across different age groups and ethnic backgrounds. This further supports the understanding that labial asymmetry is usually a normal anatomical variation rather than an anomaly?.2
Causes of Labial Asymmetry
Labial asymmetry can result from various factors, ranging from genetics to environmental influences. Below are some of the most common causes:
1. Genetics
Genetic predisposition plays a significant role in determining the size and shape of the labia. Just as other physical traits, such as eye colour or height, are inherited, so are the characteristics of the labia. This means that if a woman notices asymmetry in her labia, it may likely be that other women in her family might have similar anatomical features.
2. Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations during different stages of life, such as puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause, can significantly affect the size and appearance of the labia. Sometimes, the effects of these hormones are more pronounced on one labia than the other. Oestrogen, in particular, plays a crucial role in the development and maintenance of labial tissue. During puberty, increased estrogen levels can cause the labia to grow and change, sometimes resulting in asymmetry.
Similarly, hormonal changes during pregnancy can lead to temporary swelling and changes in labial appearance. Menopause, characterized by a decrease in estrogen levels, can cause the labia to lose elasticity and fullness differentially, potentially leading to more noticeable asymmetry.
3. Aging
As women age, their bodies undergo various changes, including a reduction in skin elasticity and collagen levels. These changes can affect the labia in varying degrees, leading to differences in their appearance. Over time, one labium may become more elongated or appear larger than the other. Aging can also contribute to a thinning of the labial tissue, making any asymmetry more pronounced.
4. Physical Activity
Activities that involve repetitive motion or pressure, such as cycling, horseback riding, or certain sports, can cause changes in the labial tissue over time.
5. Trauma or Injury
Physical trauma or injury to the vulva can lead to labial asymmetry. Such trauma can result from:
- Accidents: Incidents that cause direct impact to the genital area can damage the labial tissue, leading to asymmetry.
- Childbirth: The process of childbirth can cause significant stretching and tearing of the labial tissue. While the body generally heals well, some women may experience lasting changes in the size and shape of their labia.
- Surgeries: Surgical procedures on or near the vulva, such as episiotomies or vulvar surgeries, can lead to scar tissue formation and subsequent asymmetry.
6. Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions can cause swelling or changes in the labia, leading to asymmetry. Some examples include:
- Infections: Bacterial or viral infections can cause inflammation and swelling of the labial tissue. For instance, Bartholin’s gland cysts/abscesses, which form near the vaginal opening, can cause significant swelling on one side of the labia.
- Tumours: Although rare, benign or malignant tumours can form on the labia, causing changes in size and shape.
Understanding the various causes of labial asymmetry can help determine whether any changes are part of normal variation or require medical attention.
Signs of Concern
While labial asymmetry is typically harmless and does not necessitate medical treatment, certain symptoms can signal the need for further evaluation. They include:
1. Persistent Pain
If you experience ongoing pain, itching, or general discomfort in the labial region, it may indicate an underlying problem. Discomfort might be due to a variety of causes, such as vulvar or vaginal infections or dermatological conditions affecting the vulva. Persistent symptoms should be evaluated by a healthcare provider to identify the root cause and proffer appropriate treatment.
2. Sudden Changes
Sudden or rapid alterations in the size, shape, or appearance of the labia warrant medical evaluation. Such changes could be indicative of infections, cysts, or other medical conditions.
Rapid swelling or significant asymmetry developing over a short period is particularly concerning and should be assessed by a healthcare professional.
3. Lumps or Growths
The discovery of lumps, cysts, or other unusual growths on the labia should be promptly examined. These growths could be benign, such as Bartholin’s cysts, but they could also signify more serious conditions like tumours or abscesses.
4. Interference with Daily Activities
When labial asymmetry causes significant discomfort or interferes with everyday activities, such as walking, exercising, or sexual intercourse, seeking medical advice is crucial.3 Discomforts that impact your quality of life or ability to perform routine activities should be addressed to improve comfort and overall well-being.
When To Seek Medical Advice

If you experience any of the previously mentioned signs of concern, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional. Even if you do not have specific symptoms, but you have concerns or doubts about your labial symmetry, consulting a healthcare provider can offer reassurance.
Ultimately, reaching out to a healthcare professional can help you understand your condition better and determine the best course of action for your individual needs. Whether it is reassurance or treatment, professional guidance is crucial for addressing concerns of labial asymmetry.
Physical, Psychological and Social Aspects of Labial Asymmetry

Labial asymmetry can influence various facets of a woman’s life, encompassing physical discomfort and limitations in daily activities, psychological impacts, and social perceptions.
1. Physical Aspects
Labial asymmetry can cause discomfort or irritation during activities like sex, exercise, or wearing tight clothing, leading to chafing, soreness, or small skin tears. It may also pose hygiene challenges, increasing infection risk. Proper cleaning helps, but persistent irritation may need medical attention.
2. Psychological Aspects
Labial asymmetry can impact a woman’s self-esteem and body image, leading to anxiety or reluctance in intimate relationships. Media portrayals of the “ideal” female body often worsen these feelings. Recognizing these emotions is important, and seeking support from friends, family, or mental health professionals can help improve self-image and reduce isolation.
3. Social Aspects
Societal norms and media often portray unrealistic beauty standards, making many women feel inadequate due to labial asymmetry. This pressure can cause shame and low self-worth. Promoting open conversations and body positivity helps women embrace their unique bodies. Healthcare providers can also reassure and educate, normalizing the natural diversity of labial appearances to boost confidence.
Treatments and Solutions for Labial Asymmetry
Labial asymmetry is generally harmless and does not necessarily require medical intervention. However, for those experiencing discomfort, pain, or significant self-consciousness, both non-surgical and surgical options are available to address these concerns.
1. Non-Surgical Options
- Topical Treatments: Topical creams or ointments can relieve labial irritation and inflammation, improving tissue condition. Steroid creams reduce inflammation, while moisturizers soothe. Use these treatments under a healthcare professional’s guidance.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Adjusting daily habits can reduce labial asymmetry discomfort. Wear loose, breathable clothing to prevent friction, practice good hygiene with mild soap, and avoid activities like cycling that put pressure on the genital area.
2. Minimally Invasive Surgical Options
- Laser Treatment: Laser treatments offer a minimally invasive way to improve labial asymmetry by targeting pigmentation and texture issues. They break down excess melanin and boost collagen production, leading to a more even tone and smoother texture. Compared to surgery, lasers cause less trauma and require shorter recovery, though multiple sessions may be needed for optimal results.
- Radiofrequency Treatment: Radiofrequency (RF) treatment is an innovative non-surgical approach for addressing labial asymmetry and enhancing the appearance of the labia. This method utilizes radiofrequency energy to generate controlled heat, which promotes collagen production and tissue tightening. The procedure can be performed in a clinical setting without the need for general anesthesia. Multiple sessions may be required to achieve optimal results, and the effects can last for several months to a few years.
Both laser and radiofrequency treatments are used for non-surgical vulvovaginal rejuvenation. They both serve as an alternative or adjunct to more invasive surgical options with greater downtime, discomfort or cost.6
- Fat Grafting: Fat grafting, also known as lipofilling or vaginal fat transfer, involves transferring fat from another part of the body (such as the abdomen or thighs) to the labia. This procedure can enhance the volume and symmetry of the labia majora, creating a more balanced appearance. Fat grafting can provide natural-looking results with relatively minimal scarring. However, the long-term results of fat grafting are often unpredictable because of up to 70% volume absorption of the fat graft.7
3. Surgical Option
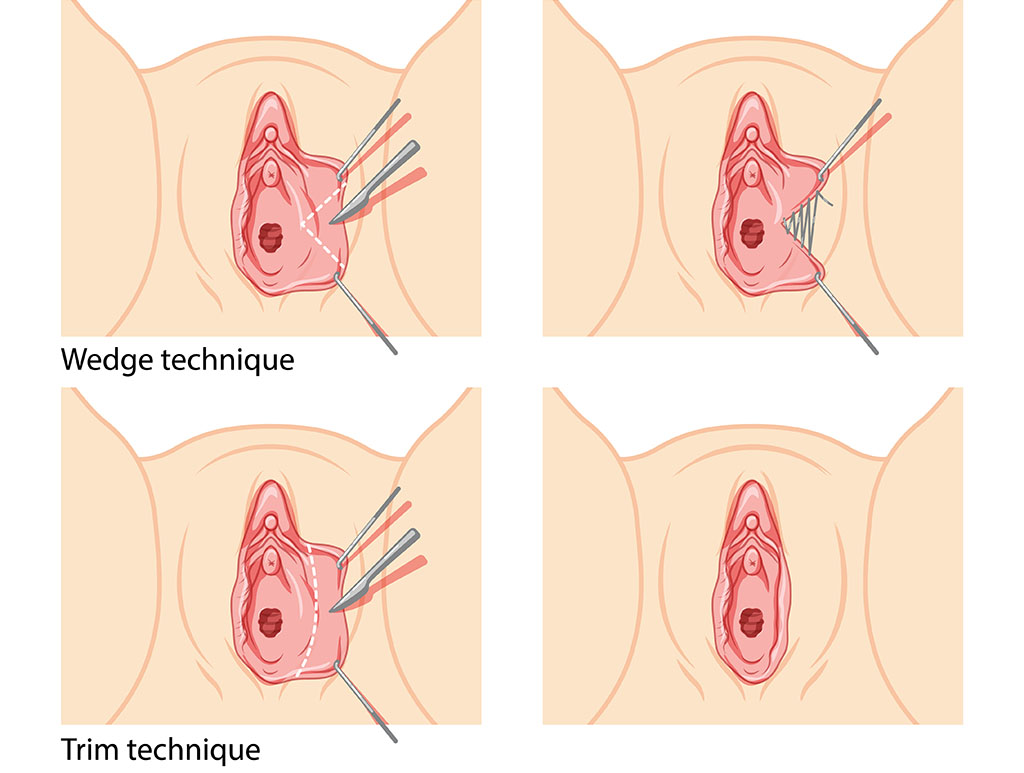
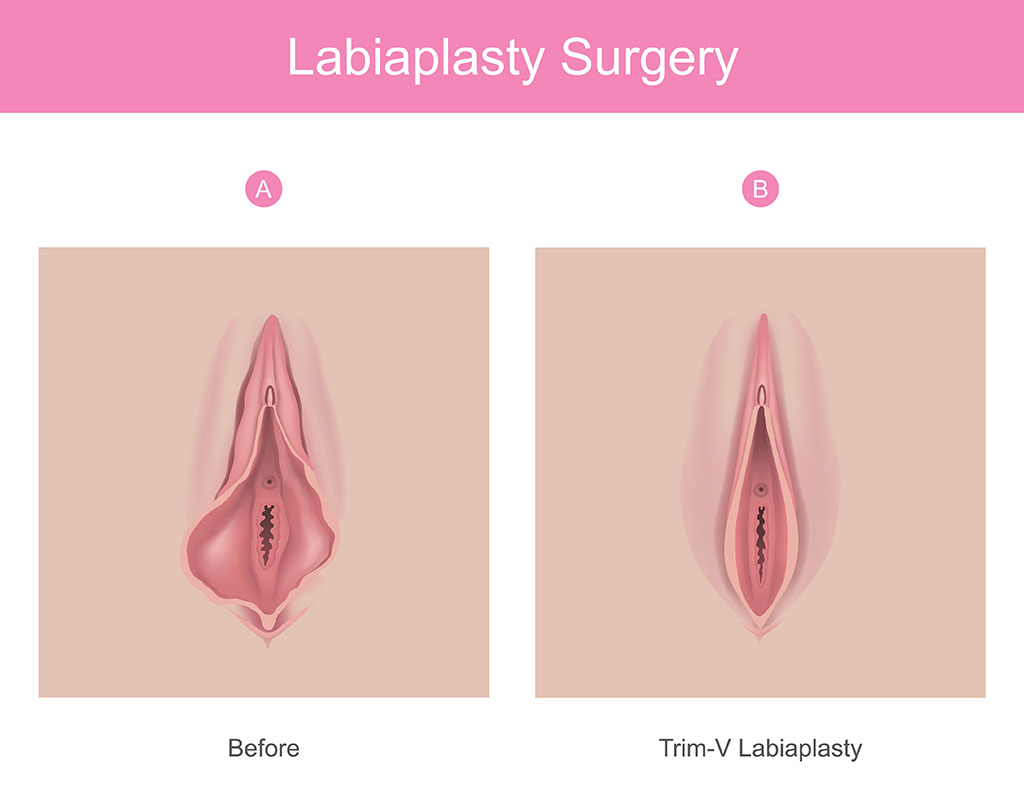
- Labiaplasty: Labiaplasty is a surgical procedure that reshapes or reduces the labia minora or labia majora to correct asymmetry and address functional and aesthetic concerns. The surgery trims excess tissue and reshapes the labial edges, typically under local or general anesthesia. Recovery is usually quick, with most patients returning to normal activities in a few weeks. Choosing an experienced surgeon is crucial to minimize risks and ensure the best results.
Risks/Complications Associated With a Labiaplasty
The following are possible adverse effects and complications that may follow a labiaplasty procedure:8
- Infection
- Occurrence of bleeding
- Formation of hematoma, leading to discomfort, pain, and swelling.
- Possibility of scarring, though this is less probable with the wedge and Z-plasty techniques.
- Temporary or permanent changes in sensation around the labia minora.
- Challenges such as poor wound healing, breakdown and separation are particularly associated with wedge labiaplasty.
- Unsatisfactory cosmetic results that may not align with patients’ expectations, potentially necessitating a revision labiaplasty.
Professional Treatment For Labial Asymmetry
Understanding labial asymmetry is key to a positive body image and informed health decisions. Though usually a normal variation, it can cause discomfort or distress. For those experiencing significant concerns, consulting a vaginal rejuvenation expert is essential. A specialist can provide a thorough evaluation and offer reassurance or treatment options to suit your specific needs.
Labiaplasty NYC is a world-renowned minimally invasive cosmetic gynecological centre. At our clinic, we specialize in vaginal rejuvenation, led by highly experienced surgeons and dedicated staff. Whether you are considering labiaplasty or other procedures, contact us today to schedule a consultation and take the first step toward enhancing your well-being.
References
- Lloyd J, Crouch NS, Minto CL, Liao LM, Creighton SM. Female genital appearance:‘normality unfolds. BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics & Gynaecology. 2005 May;112(5):643-6.
- Gulia C, Zangari A, Briganti V, Bateni ZH, Porrello A, Piergentili R. Labia minora hypertrophy: causes, impact on women’s health, and treatment options. International Urogynecology Journal. 2017 Oct;28:1453-61.
- Reddy J, Laufer MR. Hypertrophic labia minora. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2010;23:3–6.
- Koning M, Zeijlmans IA, Bouman TK, van der Lei B. Female attitudes regarding labia minora appearance and reduction with consideration of media influence. Aesthetic Surgery Journal. 2009 Jan 1;29(1):65-71.
- Perelmuter S. Labia minora hypertrophy: pathologizing diversity?. Sexual Medicine Reviews. 2024 May 15:qeae027.
- Qureshi AA, Tenenbaum MM, Myckatyn TM. Nonsurgical vulvovaginal rejuvenation with radiofrequency and laser devices: a literature review and comprehensive update for aesthetic surgeons. Aesthetic surgery journal. 2018 Feb 15;38(3):302-11.
- Simonacci F, Bertozzi N, Grieco MP, Grignaffini E, Raposio E. Procedure, applications, and outcomes of autologous fat grafting. Annals of medicine and surgery. 2017 Aug 1;20:49-60.
- Gowda AU, Chopra N, Khalifeh M. Indications, techniques and complications of labiaplasty. Eplasty. 2015;15.