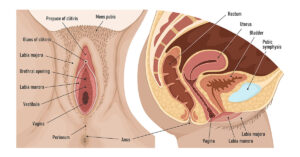
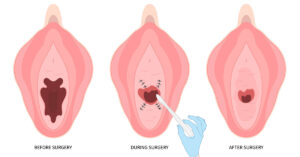
Labiaplasty is a surgical procedure that reshapes or reduces the labia minora or labia majora. While many associate it with cosmetic goals, such as improving appearance or symmetry, it can also have legitimate medical indications.
In medical terms, labiaplasty may relieve functional problems like chronic irritation, chafing, tearing, or pain during exercise, intercourse, or while wearing tight clothing. Understanding when labiaplasty is covered by insurance depends on whether the surgery is classified as medically necessary rather than elective.

In clinical practice, the distinction between cosmetic and functional labiaplasty is critical. Insurance providers typically deny coverage for procedures deemed purely aesthetic. However, labiaplasty insurance coverage may be approved when the patient experiences measurable, documented symptoms affecting physical or psychological health that cannot be managed conservatively.
Cosmetic vs. Medically Necessary Labiaplasty
Cosmetic labiaplasty aims primarily to alter the external appearance for aesthetic satisfaction. It is considered elective and self-pay. In contrast, medically necessary or “functional” labiaplasty addresses physical discomfort, hygiene issues, or recurrent infections.
Common medical indications include:
- Persistent irritation or inflammation caused by elongated labia rubbing against clothing.
- Recurrent vulvovaginal infections due to trapped moisture.
- Pain during exercise, cycling, or sexual activity.
- Labial tearing or interference with urination.
When these symptoms occur, the question of whether labiaplasty can be covered by insurance or not becomes especially important for patients seeking relief through medically necessary treatment. Insurers often require documentation proving that symptoms significantly impair quality of life. Physicians may also note attempts at conservative management, such as topical ointments, clothing modification, or pelvic floor therapy, before approving the surgical route.
How Insurers Define “Medically Necessary” Labiaplasty

Most insurance companies rely on a formal medical necessity review. The insurer evaluates medical records, physical findings, and the patient’s history of conservative treatments. For labiaplasty insurance coverage to be granted, patients typically must meet several conditions:
- Documented Symptoms: The patient experiences chronic pain, irritation, or infection directly attributable to labial hypertrophy.
- Failure of Conservative Treatments: Non-surgical management options such as barrier creams, physical therapy, and hygiene modifications have been tried without relief.
- Clinical Evidence: A gynecological or plastic surgery specialist must confirm findings consistent with the symptoms.
- Functional Impairment: The issue interferes with normal daily activities, hygiene, or sexual function.
- Preauthorization Requirements: The insurance carrier often demands preauthorization with supporting clinical documentation and photographs (taken confidentially with consent).
The American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS) notes that functional labiaplasty can be appropriate when labial tissue causes pain or medical dysfunction rather than aesthetic dissatisfaction1.
The Process of Obtaining Insurance Coverage

Patients asking if insurance covers labiaplasty should be aware that approval is not automatic, even if symptoms exist. The process usually involves several stages:
1. Verification of Benefits
Patients or clinic billing staff should contact the insurance company to confirm whether labiaplasty cost with insurance is partially or fully covered. Questions to ask include but are not limited to:
- Is labiaplasty covered under reconstructive or medically necessary surgery?
- Are there exclusion clauses for genital cosmetic surgery?
- What CPT (Current Procedural Terminology) codes apply?
However, note that coding varies by indication and technique and is jurisdiction-specific; your surgeon’s billing team should determine the appropriate CPT/ICD mapping. Avoid using vulvectomy codes for labiaplasty.
2. Clinical Evaluation
A board-certified plastic surgeon or gynecologist documents the patient’s history, symptoms, and physical findings. If the patient’s goal is to tighten labia majora skin due to functional problems rather than cosmetic preference, this distinction should be clearly documented in medical notes.
3. Preauthorization Submission
The surgeon’s office sends a preauthorization packet including medical records, physician statements, photographs, and diagnostic codes. The insurer reviews this documentation to decide whether the insurance covers labiaplasty under the policy.
4. Approval or Appeal
If denied, patients can appeal with additional supporting evidence, such as letters from other medical professionals or updated symptom records. Persistence is often necessary; insurers tend to deny initial claims if documentation is incomplete.
Typical Costs and Financial Considerations

So, will insurance cover labiaplasty completely? Rarely. Even when approved, the patient is responsible for deductibles, copayments, or coinsurance. Coverage can include surgeon, facility, and anesthesia services when medically necessary; cost-sharing and network rules still apply. Some ancillary items, such as garments, may be out-of-pocket.
If denied, self-pay labiaplasty prices start from $4000, depending on region, surgical complexity, and provider expertise. Financing or medical credit programs are often available. Discussing the full labiaplasty cost with insurance beforehand helps avoid unexpected bills.
When Labiaplasty is Not Covered
Can insurance cover labiaplasty for aesthetic purposes only?
No. Procedures performed solely to enhance appearance or symmetry fall under cosmetic exclusions. For example, if a patient’s motivation is improved self-image or confidence without documented physical discomfort, insurers classify it as elective.

Even minor discomfort may not qualify unless it is chronic, documented, and functionally limiting. Policies vary, but the burden of proof rests on the patient and surgeon to demonstrate legitimate medical necessity.
Clinical Perspective: Why Some Patients Need Labiaplasty
From a clinical standpoint, labial hypertrophy can result from genetic factors, childbirth trauma, aging, or hormonal changes. Enlarged or asymmetric labia can lead to friction, inflammation, and hygiene difficulties. Over time, these symptoms can cause psychological distress or avoidance of physical activity, which further impacts health.
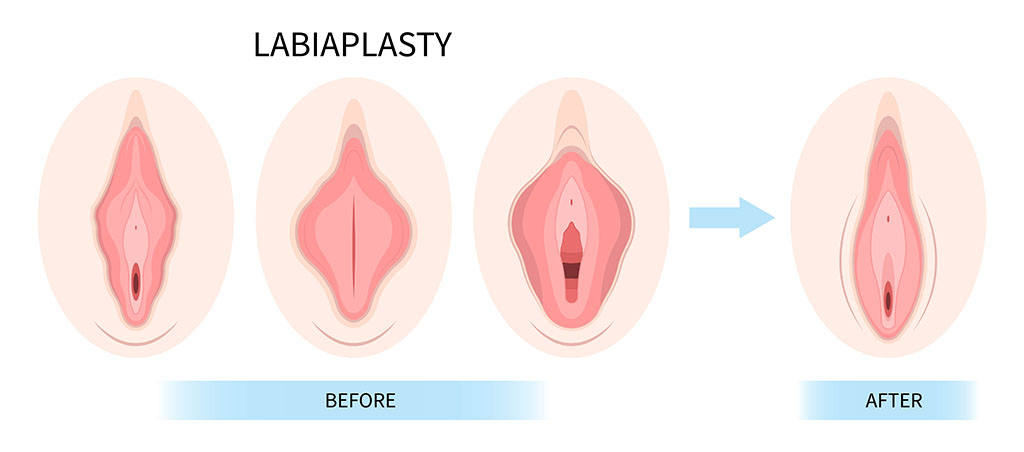
These are some of the valid reasons to get a labiaplasty beyond aesthetics. In select cases, labiaplasty improves comfort, mobility, and self-esteem by correcting tissue that impedes function. Peer-reviewed studies report significant quality-of-life improvement following functional labiaplasty, including reduced pain and enhanced satisfaction with body image2.
FAQs
1. When is labiaplasty covered by insurance?
Whether labiaplasty is covered by insurance or not depends on whether medical necessity can be demonstrated. Insurance may approve it for chronic pain, irritation, or hygiene issues that fail conservative management. Documentation from a licensed surgeon and preauthorization are essential.
2. Does insurance cover labiaplasty after childbirth?
If postpartum changes lead to functional concerns such as tearing, ongoing discomfort, or hygiene difficulties, insurance coverage for labiaplasty may be approved when medical necessity is clearly demonstrated. However, insurers often request proof that non-surgical options have failed.
3. Can labiaplasty be combined with other procedures and still be covered?
Sometimes, yes. If another procedure, such as perineoplasty or vaginoplasty, is medically indicated, it may be covered separately. However, cosmetic elements are typically excluded even if performed concurrently. Each procedure’s medical justification must be documented individually for labiaplasty insurance coverage.
Key Considerations for Patients
- Consult qualified specialists: A gynecologist or plastic surgeon with expertise in genital reconstruction can distinguish medical from cosmetic needs.
- Maintain a symptom diary: Record instances of irritation, pain, or infection over time to strengthen your medical necessity claim.
- Understand your policy: Some insurers exclude genital cosmetic surgeries entirely, regardless of symptoms.
- Prepare for partial coverage: Even when insurance coverage for labiaplasty is approved, some associated costs may remain out-of-pocket.
Restoring Function and Confidence Through Informed Care
So, is labiaplasty covered by insurance for medical reasons? It can be, but only when the condition meets clearly defined criteria for medical necessity. Patients must present thorough documentation, demonstrate that symptoms affect daily living, and show that conservative treatments have failed.

While insurers often treat labiaplasty as elective, growing recognition of its therapeutic value for certain women is shifting that perception. Working with an experienced, board-certified surgeon ensures accurate documentation, optimized surgical outcomes, and improved likelihood of insurance approval. Ultimately, the goal of medically necessary labiaplasty is not merely to reshape anatomy but to restore comfort, function, and confidence.
At our advanced vaginal rejuvenation clinic in NYC, we specialize in cutting-edge labiaplasty surgery using precise, minimally invasive techniques for optimal comfort and results. We also provide flexible payment plans to make treatment more accessible. To learn more or schedule a confidential consultation, contact our expert team today and take the first step toward renewed confidence and comfort.
References
- American Society of Plastic Surgeons. (2021). Practice parameter for female genital plastic surgery.
- Nahidi, F., Goodman, M. P., Alavi-Arjas, F., Simbar, M., Majd, H. A., & Rastegar, F. (2025). Female Sexual Function After Labiaplasty: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Aesthetic Plastic Surgery. ttps://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-025-04946-1