Pregnancy, childbirth and motherhood are marked by moments of happiness, trials and, notably, bodily transformations. Every woman’s experience after childbirth is a unique story shaped by factors like her body’s response, how the birth went, and the aftercare.
Following childbirth, it is only natural for most women to reflect on the changes their bodies have undergone. A common consideration that surfaces during this postpartum period is the matter of vaginal laxity. This post explores the several facets of vaginal tightness following childbirth, recognizing details and complexities that influence this part of a woman’s recovery post-childbirth.
What is Vaginal Laxity?
Vaginal laxity or “looseness” is a term used to describe the condition when the vagina experiences a reduction in its tightness or firmness. The two most common reasons for this are childbirth and aging. This can lead to low self-esteem for the woman as well as reduced sexual satisfaction for both the woman and her partner. Fortunately, various treatments and exercises help manage and improve this condition.
How To Address Vaginal Tightening After Childbirth
There are several methods and interventions, ranging from surgical to non-surgical procedures, that have been considered for vaginal tightening after childbirth. However, it is essential to note that the effectiveness and appropriateness of each of these methods vary and, in some cases, carry potential risks.
The following are methods that have been considered:
Surgical Option:
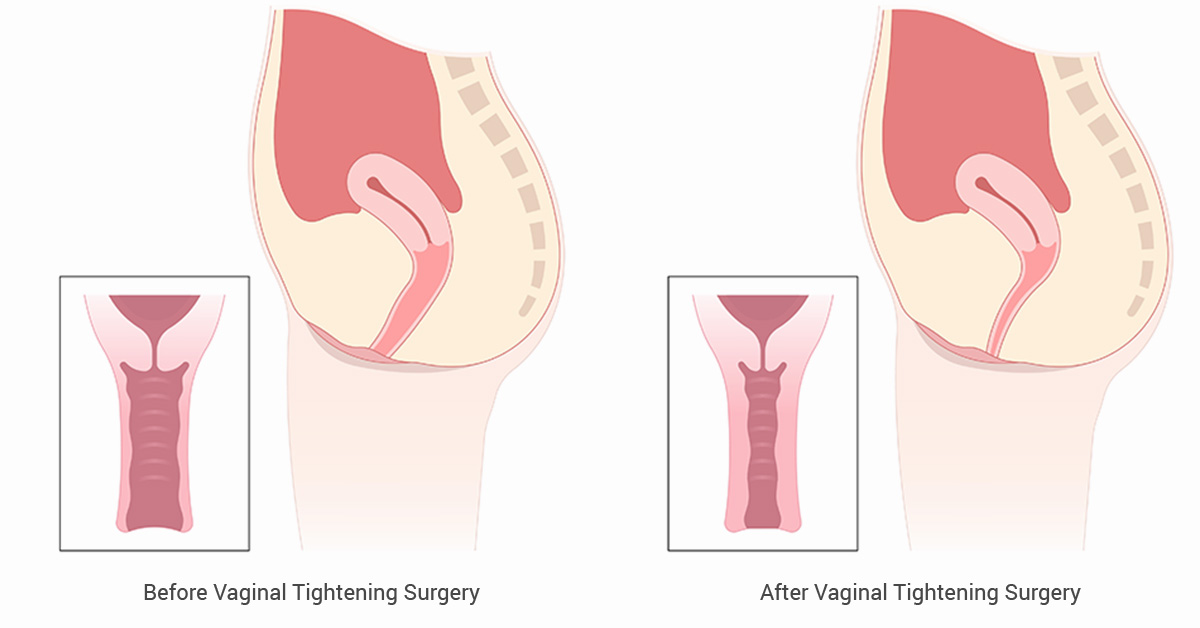
Vaginoplasty
This is a surgical procedure designed to address vaginal laxity or looseness, a condition often attributed to factors such as childbirth. The objective of vaginoplasty is to tighten the vaginal muscles and tissues, restoring firmness and tone to the vaginal canal. Below are general guidelines on how it is performed:
- Anesthesia Administration: The procedure commences with the administration of anesthesia to ensure the patient’s comfort and pain management throughout the surgery.
- Incisions in the Vaginal Canal: Under the influence of anesthesia, the surgeon makes carefully planned incisions in the vaginal canal. These incisions provide access to the areas requiring adjustment.
- Removal of Excess/Redundant Vaginal Mucosal Lining: Excess or redundant vaginal mucosal lining, often attributed to factors like childbirth and aging, is meticulously removed during the procedure.
- Tightening of Underlying Muscles: The underlying muscles of the vaginal canal, which may have experienced laxity, are then sutured together. This step is crucial for achieving the desired tightening effect.
- Suturing Process: With precision, the surgeon sutures to bring the underlying muscles together, strategically enhancing the tone and firmness of the vaginal canal.
- Closure of Incision: Once the surgeon achieves the desired outcome, the incisions are meticulously closed using dissolvable stitches. This closure is a critical step in the surgical process.
- Outcome Assessment: The surgeon assesses the results to ensure the restoration of tone and firmness in the vaginal canal is safe while aligning with the patient’s goals and expectations.
- Postoperative Care: Following the procedure, the patient receives postoperative care instructions, and the healing process is monitored to ensure a smooth recovery.
Non-Surgical Options:

1. Radiofrequency & Laser treatments
These non-surgical, non-invasive approaches used for vaginal tightening involve the use of laser or radiofrequency (RF) energy to target and stimulate the vaginal tissues. Two of the most popular treatments include ThermiVa vaginal tightening option and FemiLift.
The probe inserted into the vagina emits RF or laser energy that stimulates collagen production, tissue regeneration, and improved blood flow. In doing so, it enhances the tightness of the vagina and its elasticity after childbirth. Several sessions may be required to achieve optimal results.
2. Kegels Exercise
This is one of the most common non-surgical options that have been advocated for tightening the vagina after childbirth. Kegel exercises involve the rhythmic contraction and relaxation of the pelvic floor muscles. This non-invasive, cost-effective method has no known side effects. Conveniently, it can be done while standing, sitting, or lying down, offering flexibility to the user. Importantly, no additional equipment is required to perform Kegel exercises. Here is a guide on how to perform Kegel exercises properly.
3. Vaginal Cones
Vaginal cones, also known as vaginal weights, are a form of resistance training for the pelvic floor muscles. They are designed to help strengthen and tone the muscles, potentially contributing to improved vaginal tightness after childbirth. Below is a general guide on how vaginal cones can be used:
- Timing: it is advisable to start using the vaginal cone only after the normal flow of lochia (the postpartum vaginal discharge) has ceased.
- Selecting the right cone: vaginal cones come in various sizes and weights. It is important to select a cone of an appropriate size and weight, usually the lightest.
- Clean the cone: before use, ensure the vaginal cone is clean. Wash it with mild soap and warm water, and rinse and dry it.
- Find a comfortable position: choose a comfortable and relaxed position. This could be standing with one foot elevated, sitting on a chair, or lying down. What matters is finding a position that allows you to insert and hold the cone in place easily.
- Inserting the cone: apply a water-based lubricant to the cone for easier insertion. Gently insert the cone into the vagina with the tapered end entering first. Insert it to a comfortable depth, leaving the retrieval string outside.
- Holding the cone in place: once the cone is inserted, use your pelvic floor muscles to hold it in place. Imagine lifting the cone upward with your muscles. This is akin to performing a Kegel exercise.
- Maintain the position: aim to hold the cone in place for a specific duration, starting with a few minutes and gradually increasing over a period of time as your pelvic floor muscles become stronger.
- Gradual progression: as your pelvic floor muscles become stronger, you can progress to heavier cones to provide more resistance. This should be done gradually to avoid overexertion.
- Regular use: use the vaginal cone regularly, following a prescribed routine as recommended by a healthcare provider. Incorporate the cone exercises into your daily or weekly routine for optimal results.
- Monitor progress: pay attention to any changes in muscle strength and comfort over a period of time. Adjust the size or weight of the cone as needed to continue challenging your pelvic floor muscles.
4. Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation
Neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES) is a technique that involves using electrical currents to stimulate muscle contractions. It can be applied to the pelvic floor muscles to help strengthen and tone them, potentially contributing to improved tightness in the vagina after childbirth. Below is a general guide on how it can be used:
- Professional supervision: Neuromuscular electrical stimulation should be done under the supervision of a healthcare professional, such as a physical therapist or a specialized technician. They will ensure the correct placement of electrodes and appropriate settings for your individual condition.
- Placement of electrodes: electrodes are placed on specific areas of the pelvic floor, usually externally or internally, to target the pelvic muscles effectively. The healthcare professional will ensure the proper placement of the electrodes for optimal results.
- Adjustment of settings: the electrical stimulation parameters, including intensity, frequency, and duration, will be adjusted based on your comfort level and the therapeutic goals. These settings are usually personalized to fit your specific needs.
- Sensation and muscle contractions: you may feel a tingling or mild pulsing sensation as the electrical impulse is applied. The electrical impulses cause the pelvic floor muscles to contract and relax, stimulating the natural muscle actions during exercises.
- Progression of treatment: This procedure is typically progressive, with intensity and duration gradually increasing as your muscles adapt and become stronger.
- Combination with other therapies: Neuromuscular electrical stimulation may be used in conjunction with other pelvic floor therapies, such as Kegel exercises, biofeedback, and manual techniques to achieve comprehensive results as regards tightening of the vagina after childbirth.
5. Vaginal Tightening Gels
These gels are topical creams that have been used to improve the elasticity and firmness of vaginal tissue. They usually contain both natural and synthetic contents, e.g. hazel, allium, aloe vera and other plant extracts; however, their exact mechanism of action is unknown. Their tightening effect is usually short-lived and lasts several hours, after which it wears off. Below is a general guide on how to apply these gels:
- Wash hands with soap and water, clean and dry them before application of the gel.
- Squeeze a small amount of vaginal tightening gel onto fingertips.
- Insert fingers containing the gels into the vagina ensuring the gel is applied on the inner walls of the vagina.
- Gently massage the gel into the inner vaginal walls.
- Wait for a few minutes to begin feeling the effect.
Benefits Of Vaginal Tightening After Childbirth
- It helps improve friction and sensation during sexual activity
- Strengthens the pelvic floor muscles and improves vaginal tightness after childbirth, thus helping improve sexual experience and satisfaction for both partners.
- Addresses concerns about vaginal laxity post-childbirth and helps boost self-confidence, body image and overall well-being.
- Helps manage other pelvic floor disorders such as sexual dysfunction and stress urinary incontinence.

Get Professional Advice on Vaginal Tightening After Childbirth
While various methods, both non-surgical and surgical, are available for addressing vaginal tightening after childbirth, it is essential to approach these with realistic expectations and consult with healthcare professionals for personalized guidance. Non-surgical options like Kegel exercises, vaginal cones, neuromuscular electrical stimulation, and topical gels offer non-invasive approaches, while surgical options like vaginoplasty provide more permanent solutions.
Women considering vaginal tightening after childbirth must consult a professional. Also, it is essential to establish realistic expectations and focus on overall health and wellness. Labiaplasty NYC is a world-renowned minimally invasive cosmetic gynecological centre with top-rated reviews from thousands of clients. Book an appointment today to speak with one of our gynecological experts.




