Exploring one’s body and ensuring comfort is only normal, especially when it concerns intimate areas of the body, like the female genitalia. For many women, extra skin on the vaginal lips, medically known as “labial hypertrophy,” can be a source of physical discomfort or emotional distress. This condition, which affects women of all ages, can arise due to various reasons, including genetics, childbirth, aging, or hormonal changes.
Understanding that this condition is common is the first step in addressing concerns. Fortunately, effective solutions exist to restore aesthetics and comfort, ranging from natural remedies to medical interventions, each with unique benefits.
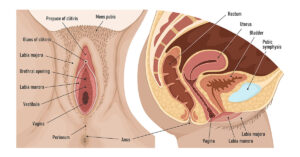
Types of Vaginal Lips

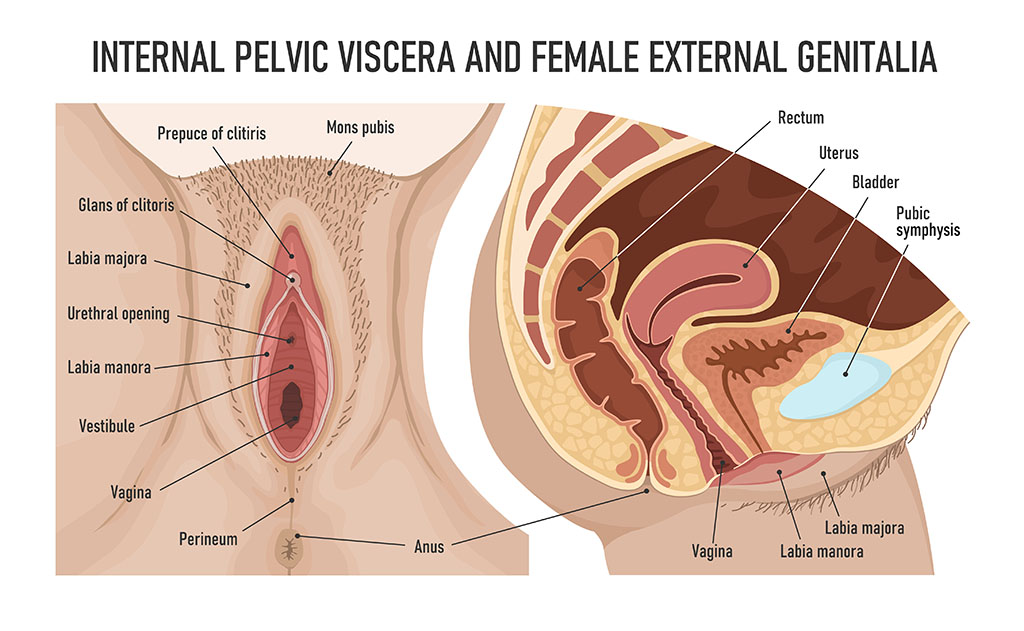
Vaginal lips are typically categorized into two main types and can vary in size, shape, and colour among individuals.
- Labia Majora: The outer lips that are larger and more padded with fatty tissue.
- Labia Minora: The inner lips that are smaller and more delicate, surrounding the vaginal opening.
Labial Hypertrophy And Its Classification
Labial hypertrophy is a condition where the labia minora (the inner vaginal lips) or the labia majora (the outer vaginal lips) are larger than usual. It can be present from birth or develop over time. While usually harmless, it can cause symptoms that lead some to seek medical advice or treatment.
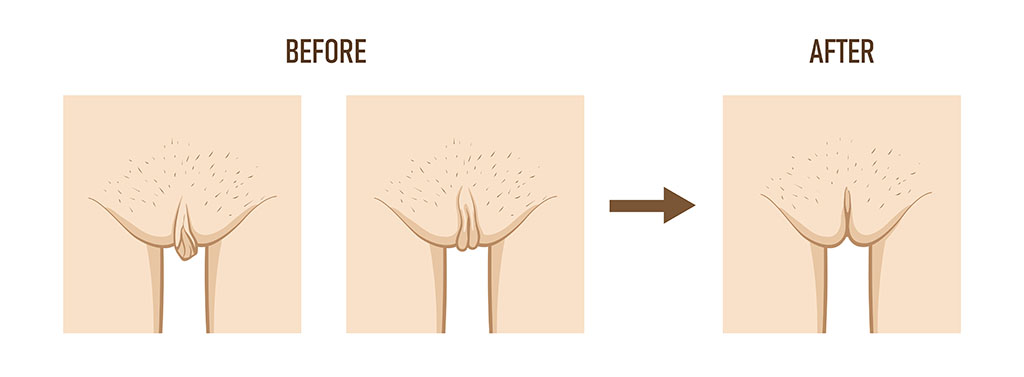
Labia minora hypertrophy has various classifications due to a lack of consensus among pediatricians, plastic surgeons, and gynecologists. Traditional systems focused on labial length and protrusion, while recent proposals emphasize patient symptoms and the relationships between the minora, majora, clitoral hood, and fourchette.1-4
According to a retrospective study5, labial hypertrophy can be categorized into three distinct and different types of vagina lips, each with unique characteristics and treatment implications. This classification system aids in tailoring surgical strategies to better meet patient needs and expectations.
Type I: Anterior One-Third Form (“Flag”)
This type of labial hypertrophy affects the front third of the labia minora and is mainly linked to aesthetic concerns and discomfort when wearing tight clothing. It usually does not cause dyspareunia (painful intercourse).
Type II: Middle Third Form (“Oblique”)
The hypertrophied prominence is at the middle third of the labia, thereby giving the whole labia minora an oblique appearance. Here, complaints usually involve discomfort with underwear and unwanted aesthetic appearance.
Type III: Posterior Third Form (“Complete”)
This type affects the posterior one-third of the labia minora and is more frequently associated with dyspareunia (painful sexual intercourse) compared to the other types.
The above classification system is known as the Banwell Classification. Unlike previous measurement-based classifications, it is based on the maximal projecting part of the labia minora and the possible symptoms the patient will experience.
Solutions And Management Options For Labial Hypertrophy
1. Minimally Invasive Options
Minimally invasive procedures are often performed on an outpatient basis, with minimal discomfort and shorter recovery times compared to surgical options like labiaplasty. These include:
Laser Therapy
This is a minimally invasive procedure that has been used for several gynecological conditions since it was introduced. Laser vaginal rejuvenation procedures use concentrated light energy to target and treat hanging vagina lips. The laser emits a precise wavelength of light that gently heats the tissues, promoting collagen remodelling and tissue tightening.6 This process can reduce the size and improve the appearance of the labia.
Benefits of Laser Therapy
- The laser allows for precise targeting of the affected area, minimizing damage to surrounding tissues.
- The procedure is typically associated with minimal pain, often described as a warming sensation.
- Patients usually experience a quick recovery and return to normal activities.
- The effects of laser therapy can be long-lasting, with many patients reporting sustained improvements.
Considerations
- Several sessions may be required to achieve the desired results.
- Patients may experience temporary redness, swelling, or mild discomfort following the procedure.
Radiofrequency Treatment
Radiofrequency (RF) treatment is another minimally invasive option that utilizes radiofrequency energy to stimulate collagen production and tighten the skin of the labia. The RF device emits energy that penetrates deep into the skin, causing controlled heating of the tissue. This stimulates the body’s natural healing response, resulting in tighter, smoother labial skin.7
Benefits
- Radiofrequency treatment is non-invasive and does not involve incisions or anesthesia.
- The treatment promotes natural collagen production, which can enhance the skin’s elasticity and firmness.
- Most patients find radiofrequency treatment comfortable, with sensations similar to a warm massage.
- There is typically no downtime required, and patients can resume normal activities immediately.
Considerations
- Similar to laser therapy, multiple sessions may be necessary for optimal results.
- Results are gradual and may take several weeks to become noticeable as collagen production increases.
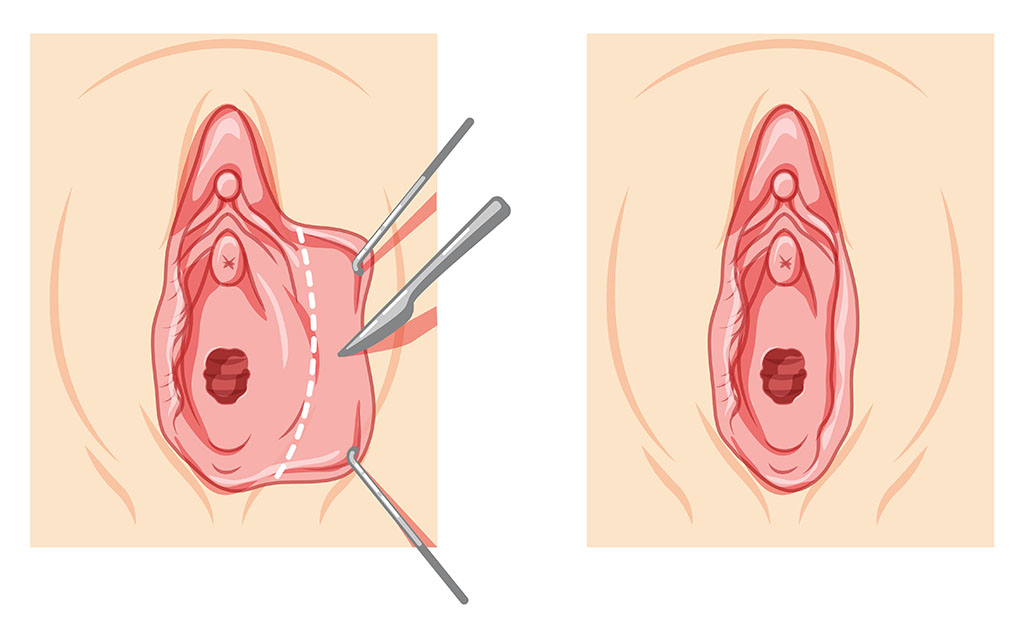
2. Surgical Option: Labiaplasty
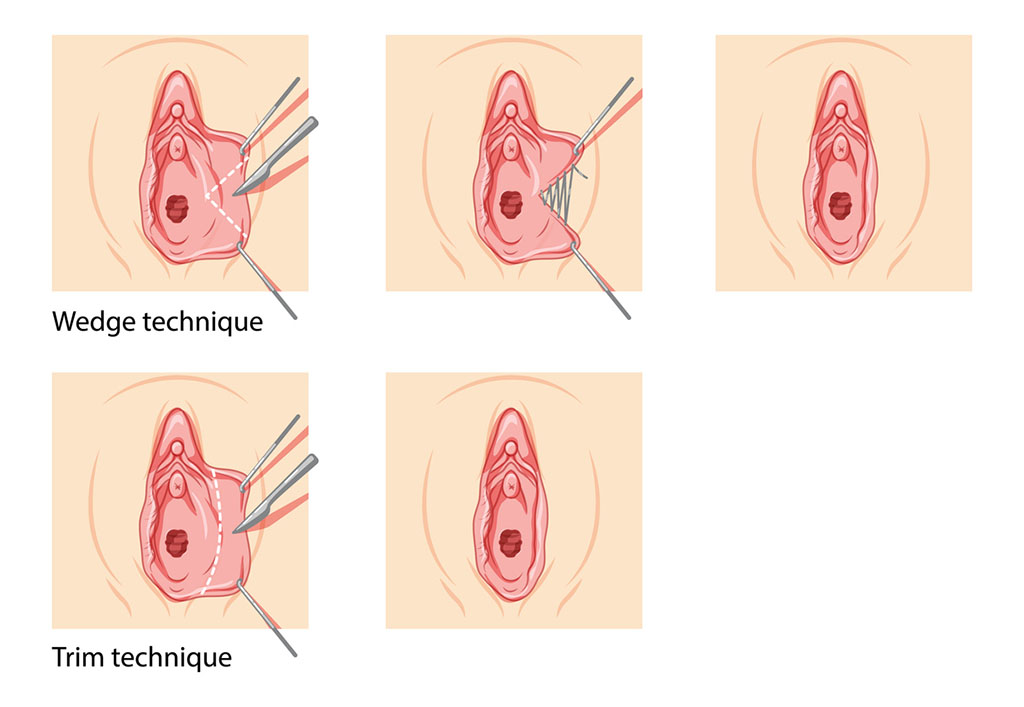
Labiaplasty is a surgical procedure designed to manage labial hypertrophy by reducing and reshaping the labia minora or labia majora. Indications for performing the procedure include physical discomfort, chronic irritation, aesthetic concerns, and functional issues. Common techniques used in labiaplasty are the trim method, wedge method, and z-plasty method, each offering unique benefits and considerations.
The procedure, typically performed under local or general anesthesia, provides enhanced comfort, improved appearance, improved self-confidence, and better hygiene. Recovery involves managing swelling and discomfort, with activity restrictions and follow-up appointments being essential. Effective labiaplasty carries few risks, such as scarring, infection, and changes in sensation, making it crucial to consult with a qualified surgeon to optimize outcomes.8
3. Conservative Approaches
- Use mild soap without harsh chemicals when bathing, and rinse thoroughly with water.
- Wear loose, breathable cotton underwear to avoid tightness and rubbing.
- Choose unscented, chemical-free pads and tampons to prevent irritation.
- Adjust labia positioning before exercise for comfort and to prevent tissue trapping.
- Consult your doctor about topical ointments and other methods to manage labial hypertrophy symptoms.
Common Causes of Labial Hypertrophy
Labial hypertrophy can arise due to various factors. Understanding these common causes can help in addressing the condition effectively.
1. Genetics
Genetics play a significant role in labial hypertrophy. This condition can be inherited, with traits passed down from parents influencing the size and shape of the labia. Just like other physical traits such as eye colour, height, and body shape, the characteristics of the labia can be inherited from one’s parents.
2. Hormonal Changes
Hormonal changes significantly influence the growth and development of the labia, particularly during key life stages such as puberty and menopause. These hormonal fluctuations can alter tissue elasticity and volume, contributing to labial hypertrophy.
3. Pregnancy and Childbirth
Pregnancy and childbirth cause hormonal changes that can temporarily swell and enlarge the labia. After childbirth, hormonal shifts and physical stretching can lead to lasting changes in labial size and shape. Multiple births increase the chances of labial hypertrophy due to repeated stretching.
4. Aging
Aging reduces collagen and elastin, leading to sagging labia. Menopause worsens this by thinning the skin, while sun exposure and smoking accelerate these changes, causing discomfort and prompting some to seek treatment.
5. Chronic Irritation
Chronic irritation from tight clothing or activities like cycling can thicken and enlarge labial tissues due to repeated friction. Infections can worsen this by causing additional inflammation.
6. Weight Gain and Loss
Significant weight gain can increase fat in the labia majora, which is influenced by hormones like estrogen. Conversely, substantial weight loss may reduce fat in the area, making the labia majora appear less full.
Symptoms of Labial Hypertrophy

Labial hypertrophy presents with a range of symptoms. These include:
- Visible Enlargement: The labia minora or labia majora may appear larger than usual. The labia minora may also protrude beyond the outer lips (labia majora).
- Discomfort or Pain: Enlarged labial tissues can cause discomfort, especially during physical activities such as exercise, walking, or sitting for extended periods. Tight clothing may also cause this discomfort.
- Irritation: The enlarged labia may rub against clothing or underwear, leading to irritation, chafing, or even skin breakdown in severe cases.
- Hygiene Challenges: There can be difficulty maintaining proper hygiene due to the size, shape and folds that may be seen in hypertrophied labia. This may increase the risk of infections.
- Psychological Impact: Some individuals may experience emotional distress or become too self-conscious because of the appearance of their labia. This can negatively affect their self-esteem and confidence.
- Sexual Discomfort: Labial hypertrophy can sometimes interfere with sexual intercourse, causing discomfort or pain during penetration.
These symptoms can vary widely among individuals, and the impact on daily life can range from mild to significant, influencing both physical comfort and emotional well-being.
Choosing the Right Option for Managing Labial Hypertrophy
When selecting the appropriate solution for managing labial hypertrophy, several factors need to be taken into account to ensure the best outcome. These factors include severity, personal preferences, and other important considerations.
Severity
- Mild Cases: For mild hypertrophy, conservative treatments like topical solutions, lifestyle changes, and minimally invasive procedures can manage symptoms and improve appearance without surgery.
- Severe Cases: Individuals with severe hypertrophy may require surgical solutions such as labiaplasty to achieve desired results. Surgical options can effectively reduce excess tissue and provide significant relief from discomfort.
Personal Preferences
- Cosmetic Goals: Surgical options like labiaplasty can offer immediate and precise reshaping of the labia, achieving specific aesthetic goals. Some other individuals may prefer a gradual enhancement of their labial tissue.
- Recovery Time: Recovery time is an important consideration for many women. Non-surgical options usually require minimal downtime, whereas surgical interventions may necessitate just a little longer recovery period.
Other Factors
- Medical History: A thorough medical evaluation is crucial to identify any health conditions that might influence treatment. Women with conditions like diabetes or hypertension may benefit from less invasive or conservative options.
- Financial Considerations: Treatment costs vary, with non-surgical and minimally invasive options generally being more affordable than surgical procedures.
- Future Family Planning: Women planning to have children may prefer less invasive treatments, as pregnancy and childbirth can still change labial size and shape. Surgery may be better suited for those done with family planning.
- Long-term Results: Some treatments are temporary, while others are permanent. Those seeking long-term results may choose surgery, while short-term relief can be achieved with non-surgical options.
By considering these factors, women can make informed decisions about the most suitable treatment for their labial hypertrophy.
Consult With A Healthcare Professional

Consulting with a gynecological expert is essential for anyone considering treatment for labial hypertrophy. During the consultation, the qualified provider evaluates symptoms, medical history, and personal concerns about labial hypertrophy. This assessment determines the condition’s severity and its effects on comfort and well-being. Based on this, the healthcare professional creates a personalized treatment plan that considers severity, preferences, and medical history.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is labial hypertrophy harmful?
Labial hypertrophy itself is generally not harmful from a medical standpoint. However, it can cause discomfort during physical activities or sexual intercourse and may lead to self-consciousness or emotional distress due to aesthetic concerns.
Can labial hypertrophy be prevented?
Labial hypertrophy often has a genetic component, meaning it cannot be prevented outright. However, maintaining good hygiene practices, wearing loose-fitting clothing, and avoiding activities that cause chronic irritation can help manage symptoms and reduce discomfort associated with enlarged labia.
What is the recovery time for labiaplasty?
Labiaplasty recovery time can vary depending on the extent of the surgery and individual healing processes. Typically, initial recovery involves swelling and discomfort that can last for a few days. Most individuals can resume normal daily activities within a few days to a week, but strenuous activities and sexual intercourse may need to be avoided for several weeks to allow proper healing.
Are non-surgical treatments effective?
Non-surgical treatments can be effective for mild to moderate cases of labial hypertrophy. These treatments aim to reduce irritation, improve tissue elasticity, and enhance the appearance of the labia without the need for surgery. However, their effectiveness may vary, and they may not achieve the same dramatic results as surgical options.
References
- Gonzalez-Isaza P. Classification of Labia Minora Hypertrophy. InTopographic Labiaplasty: From Theory to Clinical Practice 2023 Mar 9 (pp. 23-32). Cham: Springer International Publishing.
- Hamori C, Banwell PE, Alinsod RM, editors. Female cosmetic genital surgery: concepts, classification, and techniques. Georg Thieme Verlag; 2017 Apr 5.
- Motakef S, Rodriguez-Feliz J, Chung MT, Ingargiola MJ, Wong VW, Patel A. Vaginal labiaplasty: current practices and a simplified classification system for labial protrusion. Plastic and reconstructive surgery. 2015 Mar 1;135(3):774-88.
- Sorice-Virk S, Li AY, Canales FL, Furnas HJ. Comparison of patient symptomatology before and after labiaplasty. Plastic and reconstructive surgery. 2020 Sep 1;146(3):526-36.
- Smarrito S. Classification of labia minora hypertrophy: a retrospective study of 100 patient cases. JPRAS Open. 2017 Sep 1;13:81-91.
- Zipper R, Lamvu G. Vaginal laser therapy for gynecologic conditions: re-examining the controversy and where do we go from here. Journal of Comparative Effectiveness Research. 2022 Aug;11(11):843-51.
- Sadick N, Rothaus KO. Aesthetic applications of radiofrequency devices. Clinics in plastic surgery. 2016 Jul 1;43(3):557-65.
- Gowda AU, Chopra N, Khalifeh M. Indications, techniques and complications of labiaplasty. Eplasty. 2015;15.